Forwarders
Connected forwarders are displayed in the Forwarder menu. Forwarders in the list are added automatically based on the Logmanager Forwarder settings. More in the chapter Logmanager Forwarder.
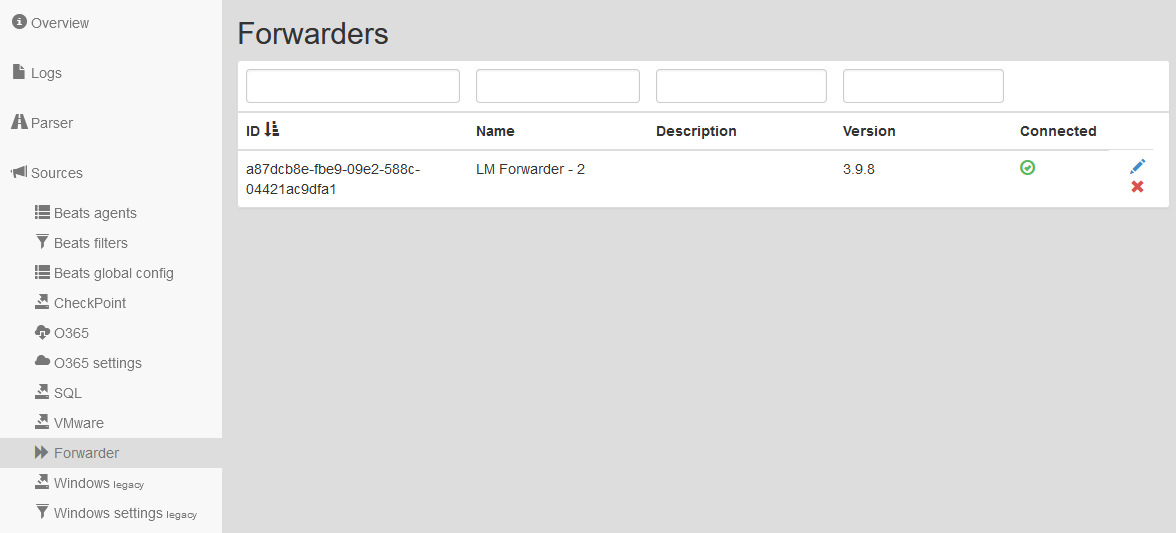
Forwarders
Table shows all the main information about connected Forwarders: unique Forwarder identification (ID), user name of Forwarder (Name), user description (Description) and installed version on the Forwarder (Version).
Filter fields are above the table. Data may be filtered by any single column. In case of using filters above more columns, the AND term is applied. A forwarder can be edited or deleted.
To edit a Forwarder, click the blue pencil icon. A form will be shown with following information:
- ID: unique identification of Forwarder.
- Name: user name of Forwarder.
- Description: user description.
- Key: authentication token from Forwarder.
- Connected: communication state between Logmanager server and Logmanager Forwarder.
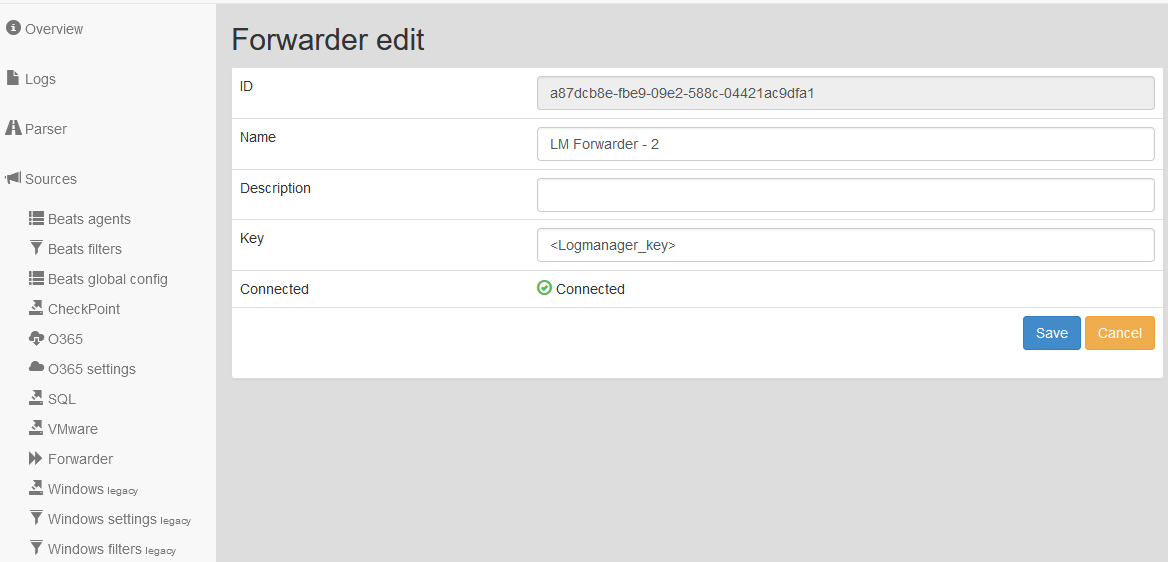
Editing Forwarder
The deletion of a Forwarder is done by clicking the red cross icon, which is shown by every Forwarder.
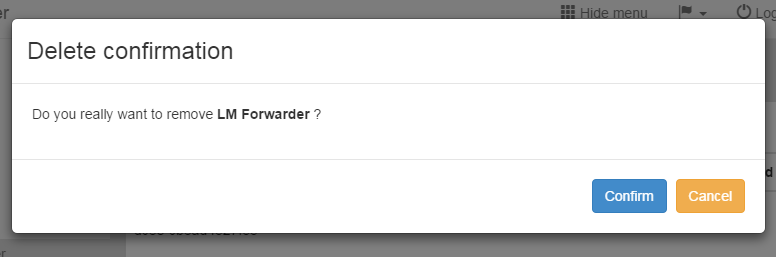
Deleting Forwarder
Important note, BEWARE of Logmanager communication between forwarders/nodes through firewalls. We recommend using blackhole for your internal subnets. All Logmanager communication is going through UDP ports. Some firewalls do not respect the routing table under certain circumstances, but use the session table to send packets to the wrong interface, causing broken communication between Logmanagers/forwarders.
Example of FortiGate misbehaving when a forwarder is communicating through an IPSEC interface to a PBX:
- UDP session is established through an IPSEC tunnel.
- The IPSEC tunnel is in a down state (Internet outage, reconfiguration, etc.), the firewall disables the routers leading to the tunnel.
- The firewall discards the session, but the UDP packets are still coming, so it creates a new session according to the current routing table (only the default route to the Internet remains).
- The IPSEC tunnel restarts and activates the route to the tunnel
- However, the session still exists on the interface to the Internet, and since UDP packets are still coming in, they are erroneously sent to the Internet by the firewall.