Logmanager Forwarder
Logmanager Forwarder is a separate device that serves as an extension of the main Logmanager server. The purpose of the Forwarder is to collect messages from the source devices on your LAN (Local Area Network) and then forward them to the main Logmanager server.
When you configure your source devices to send logs to the Logmanager Forwarder’s IP address, the Forwarder will then cache and transfer messages to the main Logmanager system.
The Logmanager Forwarder receives encrypted and unencrypted messages, logs, etc. from the devices on your local LAN and then securely forwards them as encrypted messages to your Logmanager server.
The messages received and sent by the Logmanager Forwarder retain the original identification data of the source devices including the IP address etc.
The installation of Virtual Logmanager Forwarder into VMWare and Hyper-V can be found in the Virtual Logmanager chapter.
Hardware used for the test:
- VMware ESX 6.0
- 2x Intel Xeon E5-2420v2
- 196GB RAM
- 4x 3TB SATA 7200 rpm in RAID 10.
56 virtual servers were running on ESX during the test. Testing was carried out by sending a sample of one million messages with average length of 501 characters. Messages were sent to the syslog server on a Logmanager Forwarder VM.
Logmanager Forwarder VM hardware configuration and results:
| Virtual CPU | Number of messages per second |
|---|---|
| 1vCPU Intel Xeon E5-2420v2 @ 2.2 GHz | 9000 EPS |
| 2vCPU Intel Xeon E5-2420v2 @ 2.2 GHz | 15600 EPS |
| 3vCPU Intel Xeon E5-2420v2 @ 2.2 GHz | 16000 EPS |
Network configuration can be found in the chapter Logmanager CLI.
These steps will be run im the same command line as the previous section.
-
View the results of the command:
Please enter following authentication key <Logmanager_key> for forwarder id <forwarder_id>. -
Save the returned authentication key (Logmanager_key) and ID (forwarder_id).
You should now be ready to connect the Logmanager Forwarder to the Logmanager Server.
Logmanager_IP_address is the IP address of your Logmanager server.
Logmanager_Forwarder_IP_address is the IP address of your Logmanager Forwarder.
Please continue with the following steps to add the Logmanager Forwarder to your Logmanager Server:
- Log in to the web interface of the Logmanager server.
- Go to section
Sources ‣ Forwarders.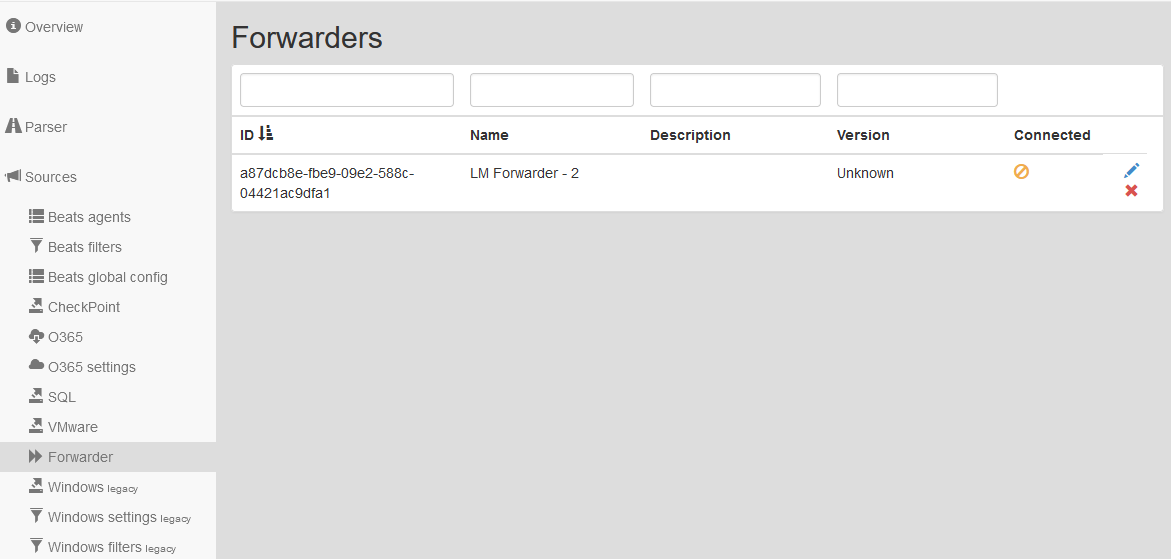
Logmanager Forwarder
- Edit the record with the ID of the set Forwarder.
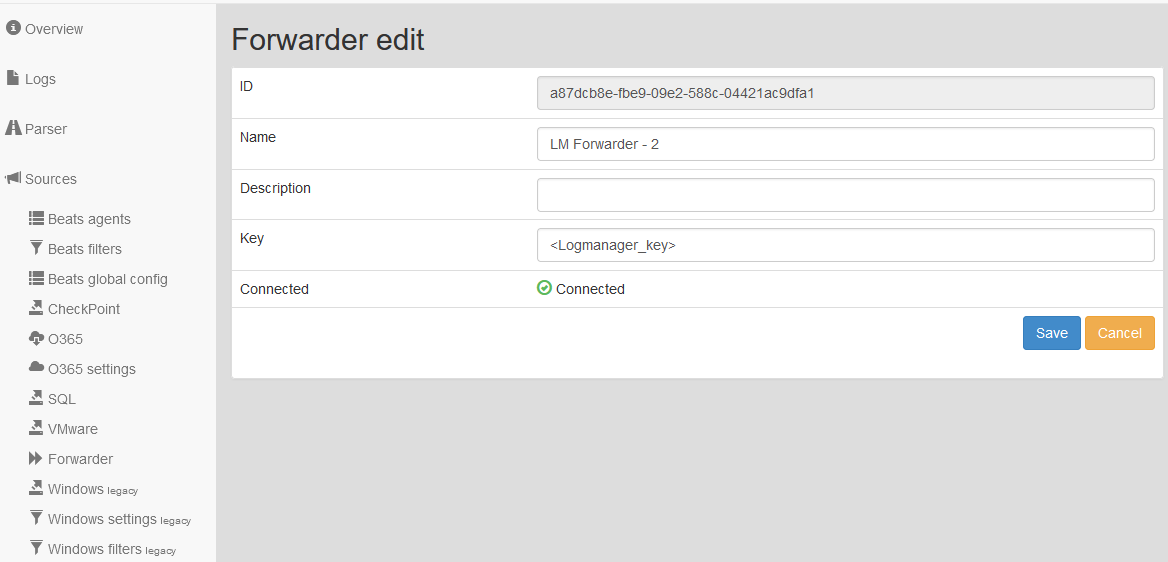
Edit Logmanager Forwarder settings
- The new Forwarder name is automatically and randomly generated, but we recommend changing to a new unique name.
- In the Key field, enter the authentication key (Logmanager_key).
- Save the record.
- In the list of Forwarders you will see the connection status (green box) and their version.
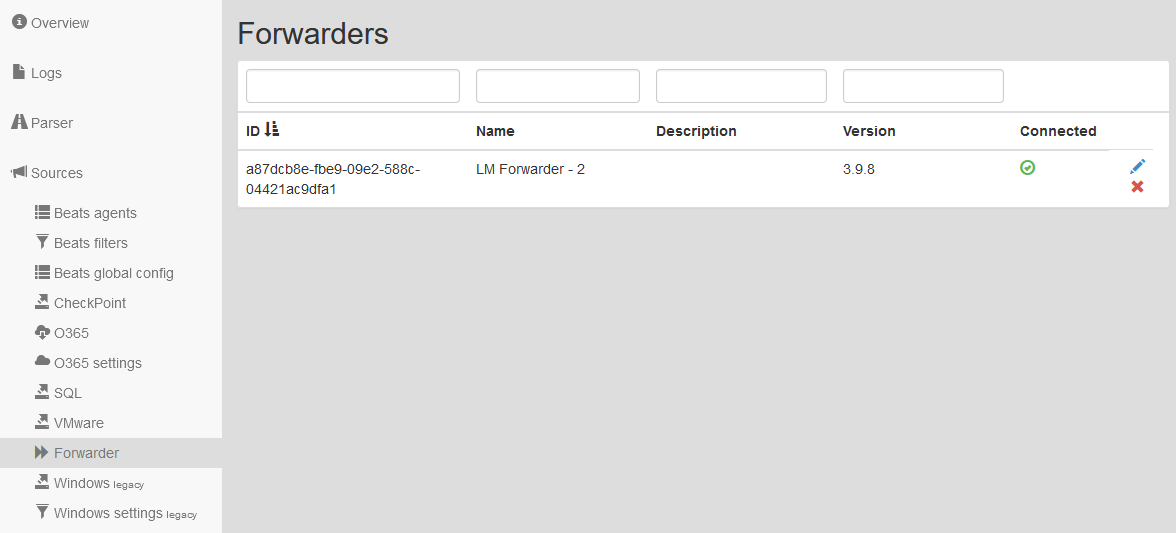
Connected Logmanager Forwarder
User accounts, NTP servers, DNS servers and more are automatically set according to the master Logmanager server configuration.
The factory setting function in the same way as Logmanager server, more information can be found in the Factory setting chapter.
The Forwarder will appear in the Forwarders List after entering the lmhost command in the CLI mode of the Forwarder. You can find more information in the chapter Forwarder settings. You may also check the chapter Communication diagram of Logmanager. The correct settings of the firewall must be configured.
Check following conditions:
- The Logmanager Server is able to successfully connect to any Logmanager Forwarders.
- The source devices are configured to send logs to the Logmanager Forwarder IP address.
- The correct classification settings in the web interface of the Logmanager server have been configured.
Be aware of any Logmanager communication between Logmanager Forwarders and their Servers through firewalls! We recommend using a blackhole for your internal subnets. All Logmanager communication uses UDP ports. Some firewalls do not respect the routing table under certain circumstances and use the session table to send packets to the wrong interface. This will cause broken communication between Logmanager Servers and the Forwarders.
Example of FortiGate misbehaving when a forwarder is communicating through a Wireguard interface to a PBX:
- The UDP session is established through a Wireguard tunnel.
- The Wireguard tunnel is in a down state (Internet outage, reconfiguration, etc.), the firewall disables the routes leading to the tunnel.
- The firewall discards the session, but the UDP packets are still coming, so it creates a new session according to the current routing table (only the default route to the Internet remains).
- The Wireguard tunnel restarts and activates the route to the tunnel
- However, the session still exists on the interface to the Internet, and since UDP packets are still coming in, they are erroneously sent to the Internet by the firewall.